What Is Acid Reflux (GERD)?
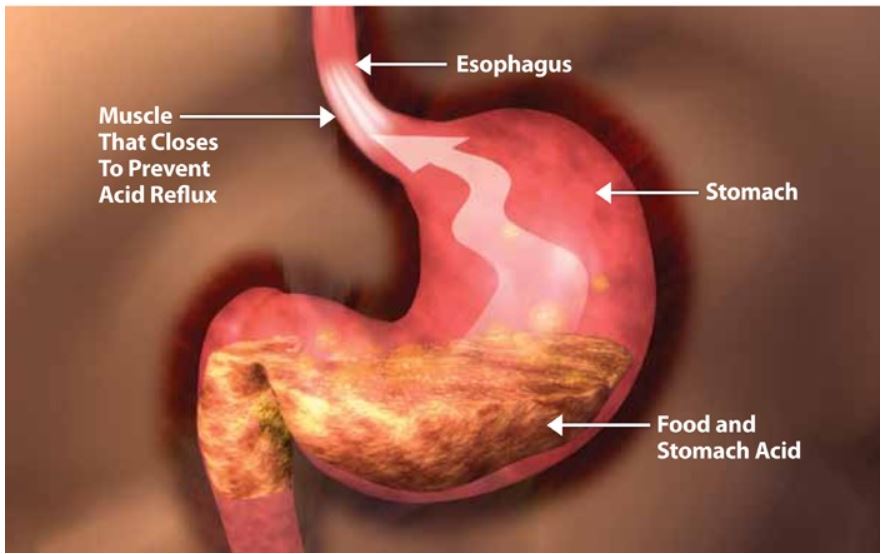
Acid Reflux is also known as GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease). It is a physical condition in which the stomach’s contents (food or liquid) leak backwards from the stomach into the esophagus. Prolonged contact of acidic stomach juices with the esophageal lining injures the esophagus and produces a burning discomfort among other symptoms.
When you eat, food passes from the throat to the stomach through the esophagus (also called the food pipe or swallowing tube). Normally, a muscular valve at the lower end of the esophagus called the lower esophageal sphincter, or LES‚ keeps the acid in the stomach and out of the esophagus. In gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD, the LES relaxes too frequently, which allows stomach acid to reflux, or flow backward into the esophagus. This acid reflux can damage the esophagus in addition to causing other symptoms.
Acid Reflux/GERD symptoms
The main symptom of GERD is frequent heartburn (also called acid indigestion). Severity can vary from an occasional mild burning after meals, to a persistent discomfort that severely limits a person’s lifestyle.
It is possible to have GERD without experiencing heartburn. Other symptoms may also include:
- Regurgitation
- Trouble swallowing (dysphagia)
- Pain with swallowing (odynophagia)
- Nausea
- Excessive salivation
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness
- A need to clear the throat repeatedly
- Sensation of deep pressure at the base of the neck. Left untreated, GERD can lead to serious internal complications resulting from injury to the esophagus. These may include:
- Reflux esophagitis-necrosis that causes ulcers near the junction of the stomach and esophagus.
- Esophageal Strictures-narrowing of the esophagus caused by reflux-induced inflammation.
- Barrett’s esophagus-chronic exposure to stomach acid causes cells in the esophageal lining take on an abnormal shape and color. Over time, this can lead to cancer.

Read More Success Stories
DISCLAIMER:
Individual result may vary.
Acidgone®
- What is Acidgone® ( aka Acid Gone® ) ?
- Is Acidgone® right for me?
- Ingredients
- Directions For Use/Smoothie Recipes
Acid Reflux
Treatment Options
- Visit www.leannclean.com to learn about our Intestinal Cleansing / Body Detox product- Lean-N-Clean®
- Read About How You Can Avoid Being a Willing Medical Victim on willingmedicalvictims.org
- Are you an independent thinker? Share your important thoughts to benefit humanity on debateandshare.com